Incontinence Treatment in Korea
SH CLINIC KOREA
Urinary incontinence is a common concern for middle-aged women!
A very common condition, affecting 1 in 3 women.
SH Clinic: Urinary Incontinence Care in Korea


What is Urinary Incontinence?
Approximately 40% of women experience urinary incontinence
Urinary incontinence is the involuntary leakage of urine from the bladder. This issue is more common among middle-aged women than men. While it might be tempting to dismiss it as a natural part of aging, proper treatment is crucial as it significantly impacts the quality of life.
sH clinic KOREA
What are the symptoms of urinary incontinence?
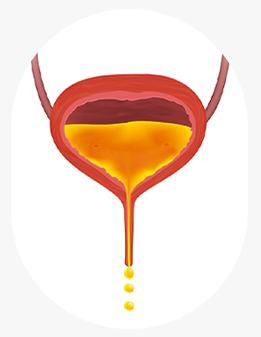
Don’t hold back any longer!
When mild symptoms of urinary incontinence appear in the early stages, it is important to visit the hospital quickly and receive appropriate treatment.
stress urinary incontinence
A phenomenon in which urine leaks when abdominal pressure increases, such as when coughing or sneezing.
urge incontinence
A phenomenon in which the urge to urinate is strong and cannot be held back, leading to leakage of urine.
mixed incontinence
A phenomenon that appears as a mixture of urgency and stress
sh clinic KOREA
The unspeakable concerns of middle-aged women
Why does urinary incontinence occur?
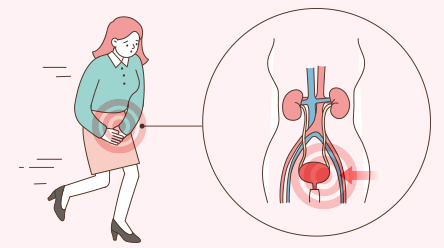
Shorter urethra compared to men
Increased abdominal pressure
Pregnancy and childbirth effects
drugs and stress
congenital anomaly
Pelvic muscle relaxation due to aging
Menopause and Hormonal Changes
Eating foods that irritate the bladder
sh clinic KOREA
How to self-diagnose urinary incontinence
Urine leaks when you cough or sneeze.
I feel pain in my lower abdomen when I urinate.
My stomach hurts when I urinate.
While going to the bathroom, I can’t hold it in and my urine leaks out.
I urinate more than twice during the night.
Not feeling refreshed even after urinating.
Urine has leaked during sexual intercourse.
sh clinic KOREA
Treatment tailored to individual causes and symptoms
How to treat urinary incontinence?
exercise therapy
How to consistently do Kegel exercises to strengthen weakened pelvic and bladder muscles
drug therapy
If the abnormality is mild and symptoms are mild, improvement can be achieved through mild drug treatment.
surgical therapy
If improvement is difficult with non-surgery, proceed according to the diagnosis of the medical staff.
Frequently Asked Questions
What treatment options are available at SH Clinic in Gangnam for urinary incontinence?
SH Clinic in Gangnam offers a variety of treatments tailored to the specific causes and symptoms of urinary incontinence. These include exercise therapy, such as Kegel exercises to strengthen pelvic muscles, drug therapy for mild symptoms, and surgical options for more severe cases.
Why is it important to seek treatment for urinary incontinence at SH Clinic?
Seeking treatment for urinary incontinence at SH Clinic is crucial because the condition significantly affects quality of life. Early and appropriate intervention can help alleviate symptoms, restore confidence, and prevent the condition from worsening, using methods tailored to individual needs.
Are there any specific qualifications or practices at SH Clinic that make it a preferred choice for treating urinary incontinence?
SH Clinic in Gangnam is known for its specialized approach to treating urinary incontinence. They offer comprehensive care that includes thorough evaluations and a treatment plan customized to each patient. The expertise in both non-surgical and surgical treatments ensures effective results for various types of incontinence.
